- June 10, 2022
- Posted by: Dyaneshwar Nirmale
- Category: Digital Meters
When choosing a current transformer, the voltage at which the electrical system is operating is a key consideration. Voltage is generally classified into low, medium, high, and extra-high as per the specific speed at which the current flows.
- Low voltage: 50-1000 Volts
- Medium voltage: 1000-35,000Volts
- High voltage: 35000-2,40,000Volts
- Extra high voltage: Above 2,40,000 Volts
Medium voltage current transformers are used to step down the high voltage power from electrical lines to a level that can be used by the consumer. Depending on the configuration of the switchgear, a fully rated current transformer should be installed on the busbars in the medium voltage section. Specific ratings for medium voltage corrent transformers are set by the IEC and NEMA/IEE. These ratings lay out certain considerations for choosing and installing the MV current transformers.
Key considerations when using a medium voltage current transformer
Proper insulation
Proper insulation is the key for medium voltage current transformers. A medium voltage current transformer could comprise up to three sets of independent secondary winding. Further, then entire assembly of the current transformer is encapsulated in resin inside an insulated casing. A medium voltage current transformer installed on busbars must be insulated at a level equal to that of the system which it serves.
Newtek Electricals has introduced a key innovation to make ,edium voltage current transformers safer, more durable and environment-friendly. Newtek medium voltage current transformers are covered with a nylon casing. Newtek nylon casing current transformers have a higher temperature tolerance than conventional transformers. Additionally, the nylon casing is flame retardant.
Explore the advantages and features of Newtek nylon casing current transformers.
Rated thermal short-time withstand current
The rated thermal short-time withstand current is the highest level of RMS primary fault current that can be handled by the current transformer both dynamically and thermally for 1 second. In the case of medium voltage current transformers, the rating of the thermal short-time withstand current should match the short-time withstand rating of the entire switchgear.
Burden and accuracy class
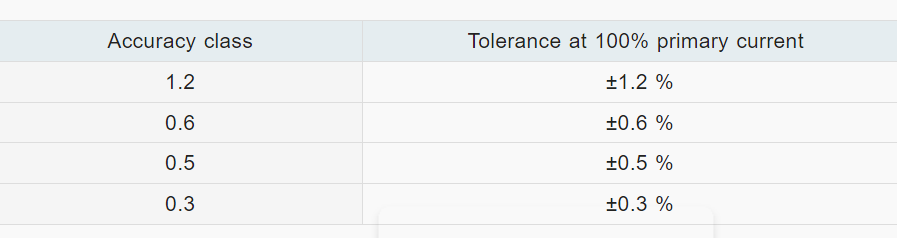
The NEMA/IEEEratings for medium voltage current transformers are chiefly used in North Ameriaca. They lay down certain requirements regarding the accuracy and burden of the current transformers. High accuracy is only guaranteed when the burden of the transformer is not exceeded.
Accuracy class for MV current transformers
Burden
Rated burden is the load burden in VA of all equipment connected to the CT secondary circuit and rated CT secondary current. Normally, the connected equipment consists of energy meter, multifunction meter, or analog meter. This load along with the load of the cable used to connect the meter is included into the burden.
Miscalculating the CT burden could lead to inaccurate reading of power consumption, or even damage the core of the medium voltage current transformer. Explore how CT burden is calculated on our blog here
