- May 8, 2021
- Posted by: Dyaneshwar Nirmale
- Category: Digital Meters
CT burden simple calculation formula
(A) Typical CTs burden values of Digital/Analog Meters

(B) How to calculate CT burden of secondary cable?
- For Copper cable
VA = k X L/S
K = 0.5 if is (secondary cable) = 5A
K = 0.02, if is = 1A
Where; L= Length of secondary cable (input/output loop) In meters and S = Cross Section Area of cables In mm .
In this case, the CTs are generally in a controlling or metering panel within a small distance from actual meter, and technically it is not necessary to have a large VA.
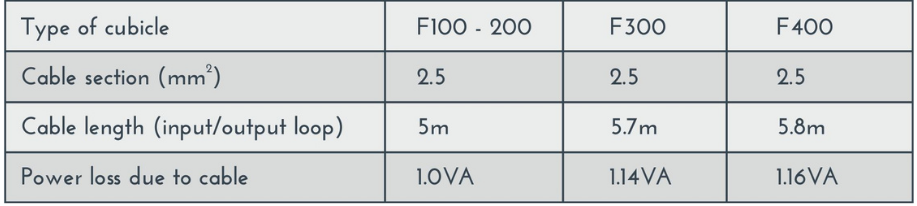
Test Case for CT 100/5A,
VA = k X L/S
K = 0.5 if is = 5A, L = 5 m, S = 2.5 mm .
VA = 0.5X 5/2.5
= 2.5/2.5
B = 1 VA
To take an example, If you connect one analog meter having a 5 meter long secondary lead cable, The total burden will be:
Burden of Meter (A) = 0.75 VA
Burden of 5 meter Cable (B) = 1VA
Total Burden A+B = 0.75+1 = 1.75VA
Multiply the total burden by safety factor 1.2
– 1.2*1.75 = 2.1VA
This means you can use a CT with 2.5VA or 5VA burden.
Conclusion
The CT burden impacts the CT accuracy. If the burden is higher than required, the CT accuracy can fluctuate.

