- August 20, 2021
- Posted by: Dyaneshwar Nirmale
- Category: Digital Meters
This one mistake in connections can turn your CTs into dangerous devices!
Current transformers do more than just enabling the measurement of high-voltage current. They contribute to enhancing our electrical safety. While protection-type CTs provide active protection from electrical faults, measuring-type CTs also isolate sensitive measuring instruments and bring a degree of electrical safety. However, miscalculation a key aspect of CT connections could endanger the site’s electrical safety, damage sensitive equipment, and increase your business costs: The CT secondary grounding.
Proper current transformer grounding is vital for the secure and smooth operation of protective relays. IEEE standard C57,13.3-2014 lays down guidelines for grounding current transformers.
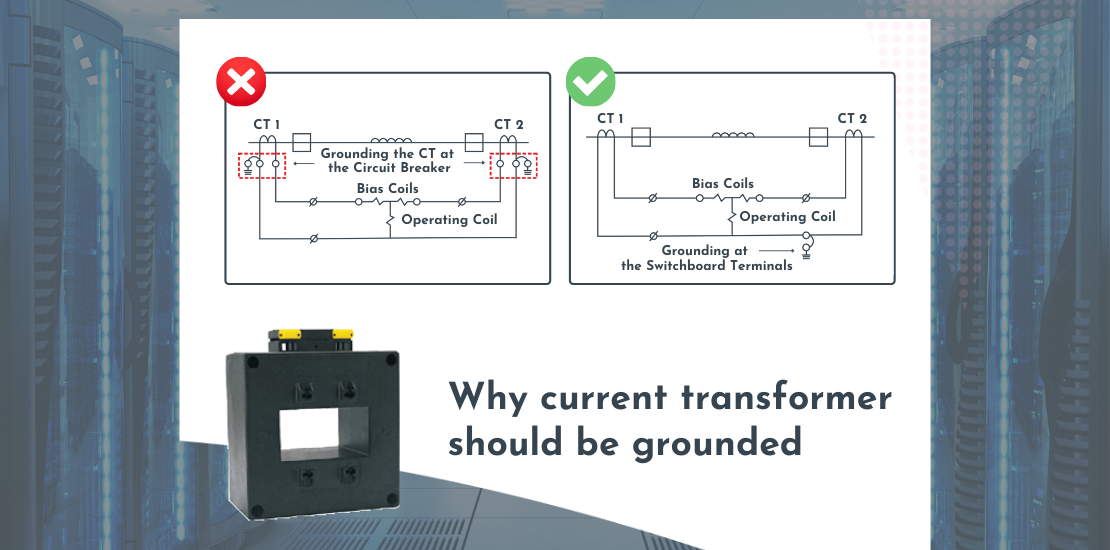
It is absolutely essential that the secondary of the current transformer should be grounded, and the grounding should be done at a single point.
Why should the current transformer grounding be done at a single point?
Current transformer secondary grounding is done at multiple points does not exactly cause any issues under normal conditions. However, in case of a fault, the potential at the different grounding points of the current transformer will rise at different rates. This leads to a high current flow through the CT circuit, and this current is not representative of the primary current. This makes the relay believe that there is a fault in its protective zone, and trip.
Such nuisance trips not only shut down the load but also lead maintenance personnel to waste time in finding fault in the differential relay when there exists none in reality.
If multiple current transformers are provided with a separate grounding, the level of a potential rise in each of the current transformers will be different. In such cases too, the relay will trip even when there is no fault in the protection zone. In order to avoid such a situation, it is recommended that the current transformer secondary grounding should be done at a single point.
How should the CT grounding be conducted?
Ideally, the point of grounding of the CT secondary should be at the first point of application or at the control board. The mounting position of the protection relay also impacts CT grounding. If the control relay is mounted at a different location from that of the CTs you could make a star connection at the breaker, but the neutral points of the CTs will have to be grounded at the relay end.
The relay must trip only when there is an actual fault within its protective zone. For reliable and sound differential protection, the star point of the CTs can serve as an ideal single point for current transformer grounding.
