- July 9, 2021
- Posted by: Dyaneshwar Nirmale
- Category: Digital Meters
What is Power Factor in an electrical network?
Power Factor (PF) is the cosine of phase angle
between voltage and current in an electrical circuit.
PF = cosine (phase angle)
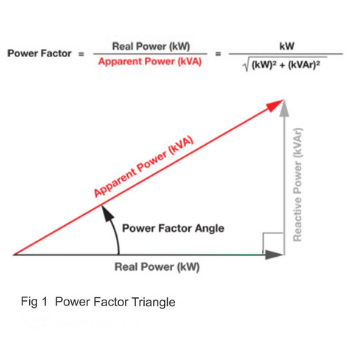
The power factor in an AC Circuits electrical power system is the dimensionless ratio of true power to apparent power, denoted as a value between -1 and 1.
Alternatively, PF is also defined as the ratio of Total Real Power to Total Apparent Power as shown in the Fig 1.
Importance of Power Factor in an electrical network
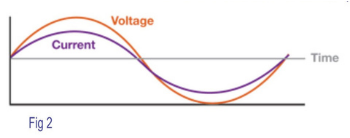
In an AC circuit, power is used most efficiently when the current is aligned with the voltage. (Phase angle = 0 PF = cos (0) = 1.0).
(Refer Fig 2.)
Hence PF is desired to be closed to unity (1.0)
However, most equipment tends to draw current with a delay (phase angle), misaligning it with the voltage. What this means is that more current is being drawn to deliver the necessary amount of power to run the equipment.
The more an equipment draws current with a delay, the less efficient the equipment is.
Refer Fig 3
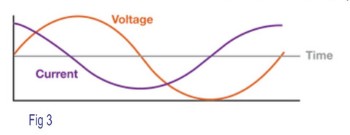
Power factor is a way of measuring how efficiently electrical power is being used within a facility’s electrical system. When Real (Active) Power = Apparent Power, and PF = 1.0 it indicates a 100% efficient system. When Active power = 0, then PF = 0.0/1.0 = 0.0.This indicates a 0% efficient system.
Conclusion
Tied to efficient use of power, PF has a direct impact on your electrical bill. For most efficient use of power, PF should be close to unity. For more details contact us: sales@newtekelectricals.com