- December 5, 2020
- Posted by: Dyaneshwar Nirmale
- Category: Digital Meters

A current transformer is maintain an accurate ratio between the currents in its primary and secondary circuits in a defined range. Current transformers thus serve to isolate power measuring instruments from high voltage circuits and supply sufficient current to protective relays. Newtek Electricals is the first current transformer manufacturer to introduce current transformers with nylon casing in India. The flame retardant nylon 66 material makes the current transformers more resistant to impact from fall and offers better protection from dust and fire hazard.
Current Transformers Working Fundamentals
The working principle of a current transformer (CT) is based on the fundamental principles of electromagnetic induction. Current transformer has two sets of windings. It receives the high voltage direct current from utility line in its primary winding and generates alternate current in its secondary winding. The primary and secondary windings are wound upon an iron core. While the primary winding is connected in series with the load, the secondary winding is connected to measuring devices. The amount of current flowing through the high powered lines into primary winding determines the number of turns the secondary winding will have. the more the current flow, the more the number of turns.
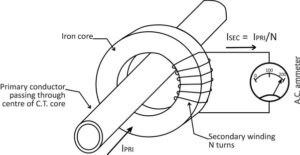
Typically, current transformers work to reduce the high voltage current to a ratio of 5 Amp or 1 Amp under normal operational circumstances. This is known as the current transformation ratio of the CT. Most CTs have a high current transformation ratio. The primary current that CTs can step down ranges from 10 Amp to 3000 Amp, and suitable devices are chosen according to the needs of various applications. Since the load impedance within the CT is very small, it works under short circuit conditions. Secondly, the current flow in CTs is not affected by the load impedance but instead depends on the current flowing in the primary winding. Newtek specializes in the production of working current transformers (CTs) and offers a variety of CT types to suit different applications. Here’s an overview of some of the CT types:
Construction of Current Transformer
A current transformer (CT) is a vital component in electrical systems used for measuring, monitoring, and protecting against overcurrent conditions. The construction of a typical CT involves several key components designed to safely and accurately transform high primary currents into manageable secondary currents. Here’s a basic overview of the construction of a current transformer:
- Primary Winding: The primary winding is responsible for intercepting the primary current to be measured. It is usually a single turn or a few turns of a thick conductor or bus bar. The primary winding is made to handle high currents safely and efficiently.
- Magnetic Core: Inside the CT housing, there is a magnetic core. This core is often made of a highly permeable material, such as laminated iron or iron-based alloys. The magnetic core is designed to concentrate the magnetic field generated by the primary current, enhancing the CT’s sensitivity.
- Secondary Winding: Surrounding the magnetic core, there is a secondary winding. The secondary winding is composed of a significantly larger number of turns of fine wire compared to the primary winding. This winding is responsible for generating the secondary current based on the primary current’s induction in the magnetic core.
- Insulation: Insulation is a crucial aspect of a CT’s construction. It is necessary to electrically insulate the primary winding from the secondary winding to ensure the safety of the measuring and control circuits. Various layers of insulation materials are used to prevent electrical contact between the primary and secondary sides.
It’s essential to note that CTs come in various designs and classes, depending on the specific application and requirements. Current transformers are used for a wide range of purposes, including metering, protection, monitoring, and control in diverse electrical systems. The choice of construction and design parameters is determined by the intended application and the conditions in which the CT will operate. Newtek supplies different types of CT, know some types of CT as follows
Types of CTs
Current transformers can be classified according to the use cases such as indoor or outdoor, and according to the purpose such as metering and protection type CTs. Metering and protection type CTs are designed specifically for their stated purpose and should not be used interchangeably.
Protection type Current Transformer
Protection type CT are designed to monitor current during a fault in the electrical system. They will then give the input to the relay which will trip the circuit breaker to keep vital loads isolated. These CTs can function when the current flow is 10-20 times the rated current, and are not saturated during electrical faults. As the amount of current flowing through the protection type transformers is high, connecting it to the meter which is not designed for such high levels of current will damage the meter.
Metering type CTs
Accuracy and safety are the two key features of a metering CT. Metering CTs are connected to the meters that measure power consumption. Because of this, they come with a designated Instrument Safety Factor (ISF). The core of the CT saturates if the current is higher than rated current, and this protects the meters from being damaged. The same will happen if a metering CT is deployed for protection. As the core of the CT saturates, the secondary current will be distorted and might prevent the relay from operating.
CT types according to construction
Based on their construction, current transformers can be classified into the following types
Wound type ct
Wound type current transformer has the basic make of primary and secondary windings. These windings cannot be disconnected This current transformer is noted for its high accuracy.
Bar type ct
In bar type current transformers, a bus bar of the main circuit is used as a primary winding. They are usually bolted to the device that carries the current and are isolated from high operating voltage in the system. Magnetization of the core can reduce their accuracy.
Window type ct
The window type current transformers lack any kind of primary winding, and their secondary winding is situated around the conductor through which the current is flowing. Current is induced in the secondary winding by the magnetic electric field which is created by the current flowing through the conductor.
Bushing current transformer
The bushing current transformer is very similar to the bar type transformer. In this CT, the core and secondary are located in the place of the primary conductor. The secondary winding can be twisted into a circular or annular shaped core. This in turn connects to high voltage bushing inside the circuit breakers. The bushing works as primary winding when the conductor flows through it. An insulating bush can be arranged to work as a core. These types of current transformers tend to be cheap and are reused for relaying purposes in high-voltage circuits.
CT manufacturer and supplier
When current transformers are damaged, their replacements takes up considerable time. In that light, providing more durable, and high-performing CTs is a key concern which Newtek Electricals addresses efficiently. We have introduced current transformers with nylon casing which can deliver reliable performance in harsh conditions. Newtek has proven experience and expertise in providing quality CTs at large scale in sectors such as steel, cement, infrastructure, petroleum and power-in short lead times.
To avail of durable, reliable and high-performing current transformers, reach out to us at sales@newtekelectricals.com or call on +91 – 93728 62651, 93728 62635
