- May 8, 2021
- Posted by: Dyaneshwar Nirmale
- Category: Digital Meters
What is Phase Angle in an Electrical Network?
Phase Angle is the angle between voltage and current in an electrical circuit. When capacitors or inductors are involved in an AC circuit, current and voltage do not peak at the same time. The fraction of a period difference between the peaks expressed in degrees or radians is the phase difference or phase angle.
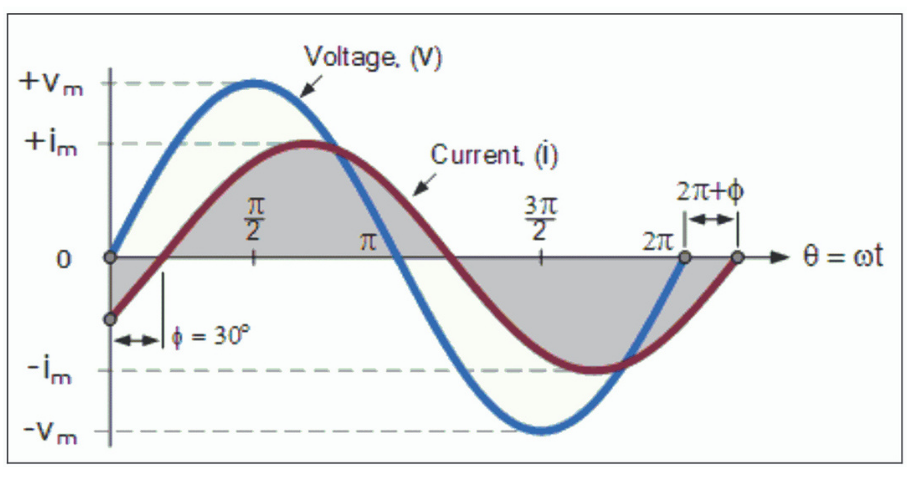
It is customary to use the angle by which the voltage leads the current. This leads to a positive phase for inductive circuits since current lags the voltage in an inductive circuit. The phase is negative for a capacitive circuit since the current leads the voltage.
The phase angle(Ø) is usually measured in degrees or radians.
The following diagram shows a phase shift or phase angle of 30 degrees between the voltage and current.
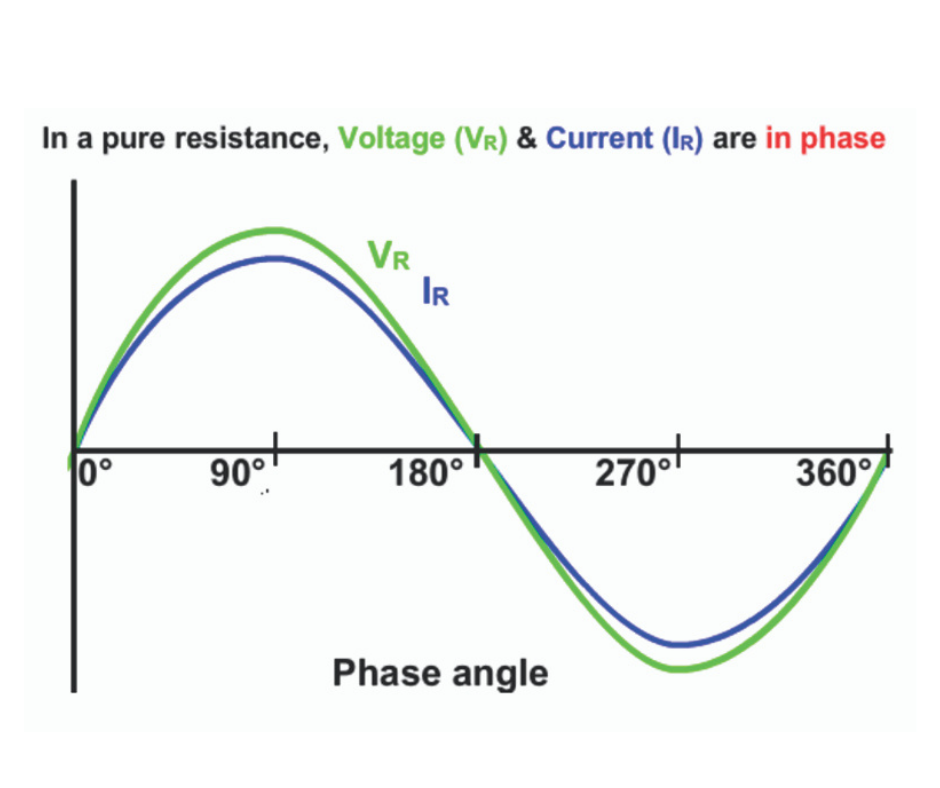
For purely resistive loads, there is no phase shift between voltage peak and current peak. Hence, phase angle (Ø) is 0 degree (360 degree)
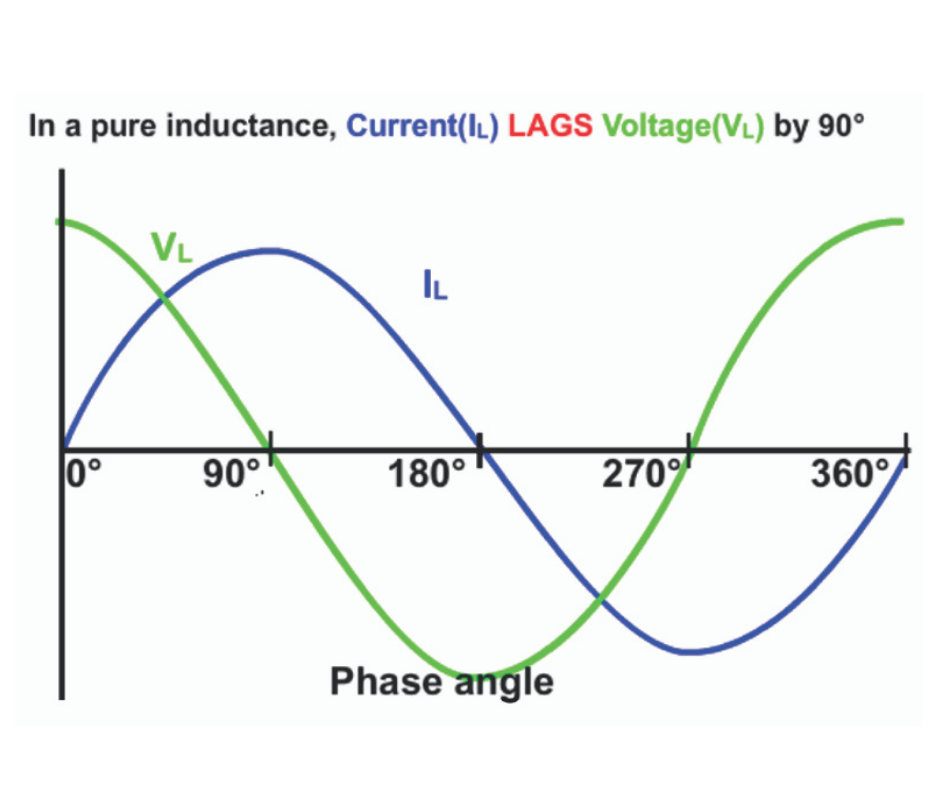
For a purely inductive load, the current lags the voltage by phase angle (Ø) of +90 degree.

For a purely capacitive load, the current leads the voltage by 90 degrees (or Voltage lags the current by 90 degrees) Hence please angle (Ø) is
Conclusion
Phase angle can stand anywhere from 0 to 360 degrees depending on the type of load and the quadrant in which the circuit is working. It is a key indicator of system stability and must be checked when two sources have to be connected to avoid inverse current.